Different Types of CNC Machining and Their Applications
Understanding CNC Machining: Definition and Basics
CNC machining, which stands for Computer Numerical Control machining, basically works when computers tell machines what to do so they can make really precise parts based on designs. What makes this method special is how it takes away material bit by bit from raw stock until what's left matches exactly what was drawn on screen. Think of it like turning computer files into actual objects sitting right there on the workbench. One big plus? It creates super detailed parts that would either take forever or just not be possible if someone tried doing all that cutting manually. Look at any airplane manufacturer or car factory, they're all over CNC tech because nothing else comes close to matching those tolerances. Even hospitals depend on these machines for making surgical instruments where even tiny mistakes could mean life or death situations.
CNC tech actually started taking shape way back in the 40s and 50s when engineers first began experimenting with numerical control machines that used those old school punched tape systems for programming. When computers came along, everything changed pretty dramatically for these machines. What was once all manual work got turned into something much more automatic. The improvements weren't just about being more accurate either they completely transformed how factories operated. Mistakes made by humans dropped off a cliff while production speeds shot through the roof. Fast forward to today and CNC machining has become absolutely essential across countless industries. Manufacturers keep finding new ways to push this technology further every single day, making things we never thought possible just another Tuesday on the shop floor.
Core Components of CNC Machines
To really get how CNC machines work, knowing what makes them tick inside is pretty important when looking at manufacturing efficiency. At the heart of every CNC setup sits the Machine Control Unit, or MCU for short. Think of this part as the brain behind all those complex movements. When programmers feed in code like G-code or M-code, the MCU takes that information and turns it into exact directions telling different parts where to move. Without this translation process, getting the kind of precision needed in modern manufacturing wouldn't be possible. Beyond just moving things around, the MCU handles other stuff too. Coolant systems need to kick in at certain points during cutting operations, and the spindle has to spin at just the right speed. These aren't minor details either they're actually vital parts of making sure everything runs smoothly throughout the whole machining cycle.
CNC machines rely on various input devices to get designs and commands into the system. Common options range from standard keyboards and computer mice to sophisticated touch screen interfaces that many modern shops now use. When operators enter data through these systems, they're essentially feeding instructions directly to the machine's control unit so it knows exactly what needs doing. Getting this right matters a lot because even small mistakes can throw off entire production runs. That's why most manufacturers invest time training staff properly on their specific equipment inputs, since accurate data entry makes all the difference between a successful operation and costly rework down the line.
In CNC machines, the drive system handles all the actual moving parts, basically what makes the cutting tool do its thing. Motors and those ball screw assemblies team up to push the tool along set routes during operation. When talking about precision, feedback mechanisms really matter alongside the drive system. These feedback systems keep an eye on where exactly the tool is positioned plus track various operational stats, then send that info back to the main control unit. The constant stream of data lets the MCU tweak things as needed so cuts stay accurate no matter how complicated the design gets. Put it all together and we get this coordinated setup that's at the heart of how CNC machines actually function day to day.
Types of CNC Machining: An Overview
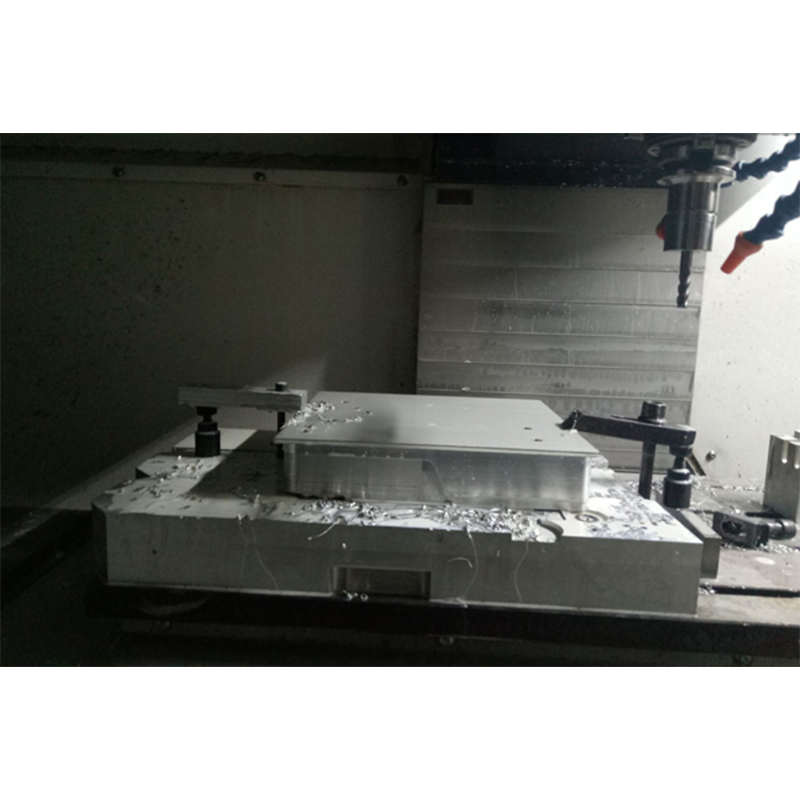
In the realm of CNC machining, there's quite a range of equipment built for different jobs, each aiming at high accuracy. Take CNC milling machines for instance they stand out as really flexible tools that use rotating cutters to shape all sorts of materials into exact forms. What makes them so valuable is their ability to tackle everything from basic shapes to complicated parts, which explains why manufacturers in fields like aircraft production and car manufacturing rely on them so heavily when getting things just right matters most. With multiple axes in operation, these machines can produce detailed components while wasting far less material compared to traditional methods.
CNC turning machines basically make round parts by spinning the material while cutting tools shape it down to exact measurements and smooth surfaces. These machines are really good at making things like drive shafts and bearing housings that we see all over cars and airplanes. What makes them so versatile is their ability to work whether mounted vertically or horizontally depending on what needs to be machined. Shops often switch orientations based on part size and complexity, which gives manufacturers flexibility when tackling different production runs.
When working with materials like wood, plastic, or composite boards, CNC routers and laser cutters offer some really good options. Both types can tackle complicated shapes and detailed cuts without wasting much time. The routers themselves are built for three dimensional work, which is why they show up so often in shops making things like furniture with fancy carvings. Laser cutters take a different approach though, using concentrated light beams to slice through material cleanly. They're great for things like engraving logos on metal parts or cutting out delicate patterns from acrylic sheets. Because these machines handle so many different tasks, they've become pretty essential across various fields. Sign makers rely on them daily, just like jewelers who need exact measurements when crafting custom pieces. No wonder so many workshops now have at least one of these tools sitting around.
Applications of CNC Machining in Modern Production
CNC machining plays a major role in the automotive sector, making possible the creation of complicated parts that need exact measurements. Manufacturers rely heavily on this tech when producing things like engine blocks, transmission components, and structural pieces that require tolerances as tight as thousandths of an inch. What makes CNC so valuable isn't just about getting dimensions right it's that precise manufacturing leads to better performing vehicles while reducing failure risks over time. Car makers know that even small deviations can cause big problems down the road, which is why they invest in these advanced machining processes.
The aerospace sector depends pretty much on CNC machining when it comes to hitting those tough safety and reliability benchmarks. Parts made for planes need incredibly tight tolerances sometimes down to just 0.001 inch, something regular machining methods simply cant match. Take turbine blades or landing gear components for instance these are pieces where getting the measurements right matters a lot. A tiny mistake here could mean big trouble later down the line for both pilot safety and how well the plane performs overall.
CNC machining plays a vital role in making medical devices because it delivers both accuracy and consistency needed for complex parts like surgical tools and implantable devices. Medical components require extremely tight tolerances and materials that won't react badly inside the body, which is why they need to pass rigorous quality checks before reaching patients. What makes CNC machining so valuable is how it can create implants specifically designed for each person's unique anatomy. This capability has been game changing for doctors who want to offer treatments that fit better and work more effectively than generic options.
Product Showcase: Examples of CNC Machined Parts
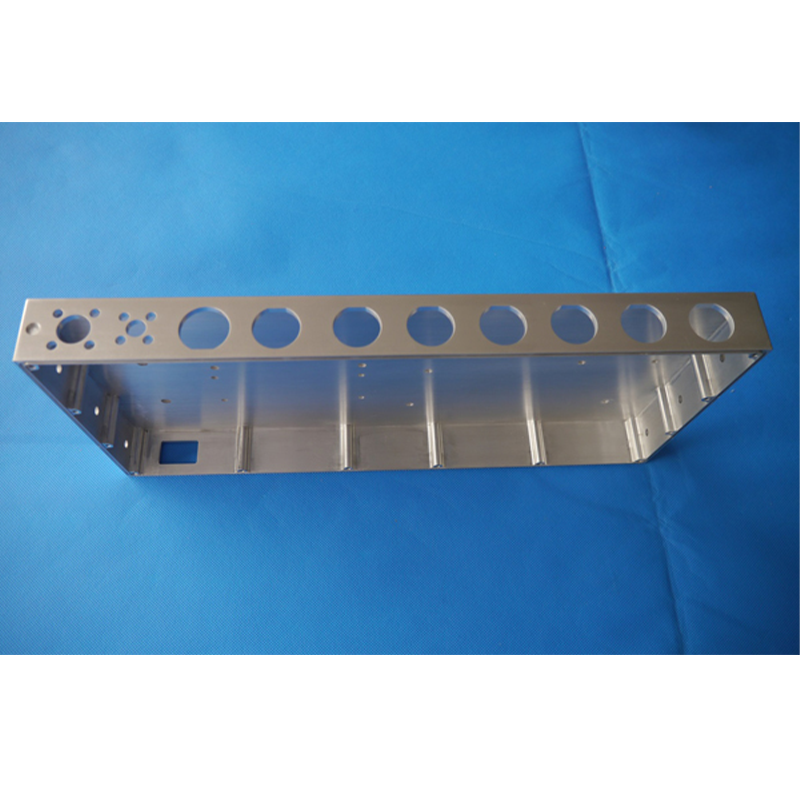
Looking at the 150 sets of precision CNC machined parts made for wireless infrastructure across England gives us a good example of how CNC machining works when making essential components. These parts show just how well CNC can handle large production runs while still maintaining quality and strength needed for tough wireless network requirements. When it comes down to it, getting both precise measurements and lasting materials matters a lot for these components to fit properly within complex wireless systems without causing problems later on.
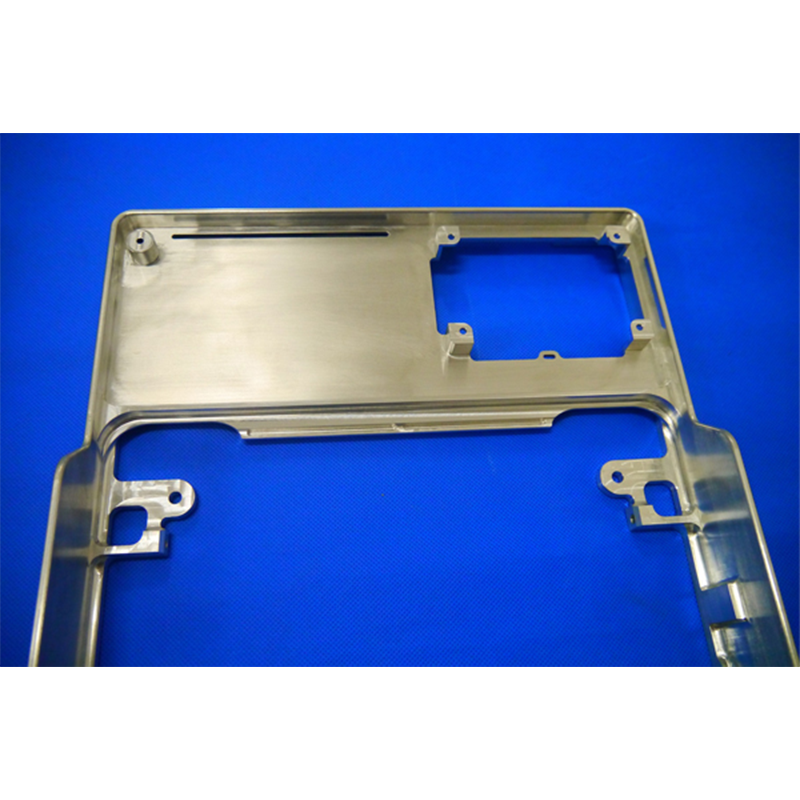
Take for instance the 100 set batch of Aluminum 6082 CNC machined frame parts produced for video intercom devices across the US market. These parts highlight how versatile CNC machining can be when it comes to making components for electronic equipment. Made from the durable yet light Aluminum 6082 alloy, they strike just the right balance between being strong enough to withstand daily wear while remaining lightweight enough not to burden installation crews. The fact that manufacturers can get exactly what they need in terms of dimensions and specifications speaks volumes about why so many tech companies rely on CNC machining processes today. After all, when building something as intricate as a video intercom system, getting those measurements right matters a lot.
Moreover, Customized machining services for CNC turning and milling present opportunities for businesses to obtain components tailored precisely to their operational needs. Customization through CNC machining provides flexibility, allowing companies to meet specific technical and performance criteria, encouraging innovation and efficiency in various industries.
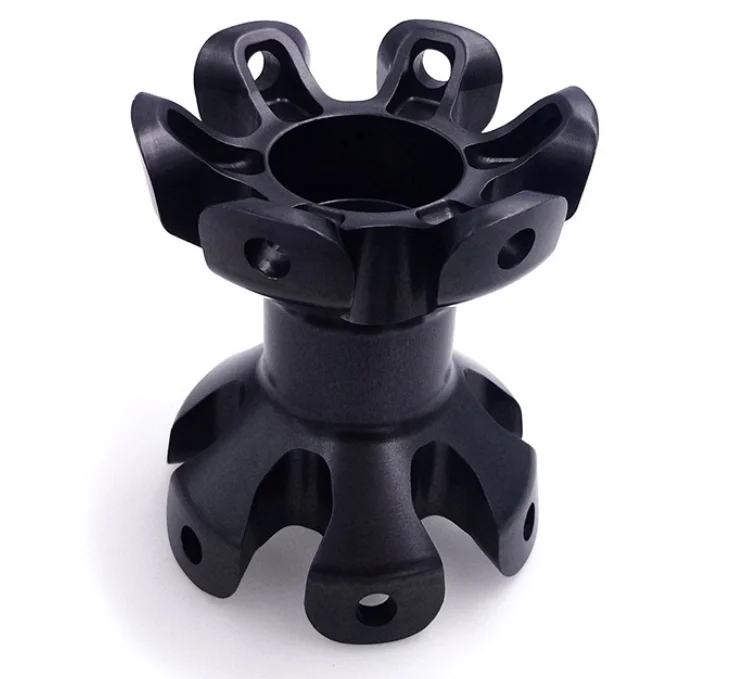

Benefits and Challenges of CNC Machining
CNC machining brings some major benefits to the table including better productivity rates, products that look the same every time they come off the line, and the ability to make really complicated shapes that just aren't possible when someone is doing it by hand. When machines are controlled by computers, they can follow even the most detailed design specs exactly, which means factories run much smoother and faster than before. Take aerospace parts or medical implants for instance these require extremely accurate measurements and repeatable results something traditional methods simply cant match. The difference in precision makes all the difference when building components where even tiny errors could lead to big problems down the road.
CNC machining comes with its share of headaches too. Machines need constant upkeep if they're going to keep running smoothly, and even small programming mistakes can bring everything to a halt. Good operators aren't just nice to have they're absolutely critical for keeping things running right when problems pop up. Most newcomers find themselves stuck in a steep learning curve because mastering CNC means getting comfortable with both the computer code side and the hands-on work at the machine itself. That's why most shops invest heavily in training programs these days. Without proper education and continuous practice, operators simply won't be able to handle all the complexities modern CNC systems throw at them.
Future Trends in CNC Machining Technology
The latest developments in automation and artificial intelligence are transforming how CNC machining works today. These new tech tools cut down on mistakes made by people, boost output rates, and make shop floor operations run smoother than before. When manufacturers integrate AI into their CNC systems, they get smarter machines that figure out better cutting routes and spot when parts might fail before breakdowns happen. This means fewer interruptions during production runs and generally faster turnaround times for machined components across different industries.
Bringing IoT into manufacturing has changed everything when it comes to monitoring and controlling CNC machines. With IoT, manufacturers can collect and analyze data in real time, which makes their production processes much smarter overall. The connected systems also help with maintenance work because the machines themselves can warn operators about problems long before anything serious happens. What we're seeing now is that CNC machining isn't just getting better at what it does, but actually becoming something entirely different - an intelligent system that adapts to changing conditions on the factory floor rather than simply following pre-set instructions.

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 BG
BG
 HR
HR
 CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 IW
IW
 LV
LV
 SR
SR
 SK
SK
 UK
UK
 GL
GL
 HU
HU
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 FA
FA
 GA
GA
 CY
CY
 EU
EU
 BN
BN
 BS
BS
 LA
LA
 NE
NE
 SO
SO
 KK
KK













